

Sudo chown mongodb:mongodb -R /var/lib/mongodbĪssuming you installed the mongodb server using a standard method on standard linux system, you will likely need to restart the service using the systemctl (SystemD) or service (upstart) command. To solve this either make mongodb the owner
#MONGODB SERVICE START UBUNTU INSTALL#
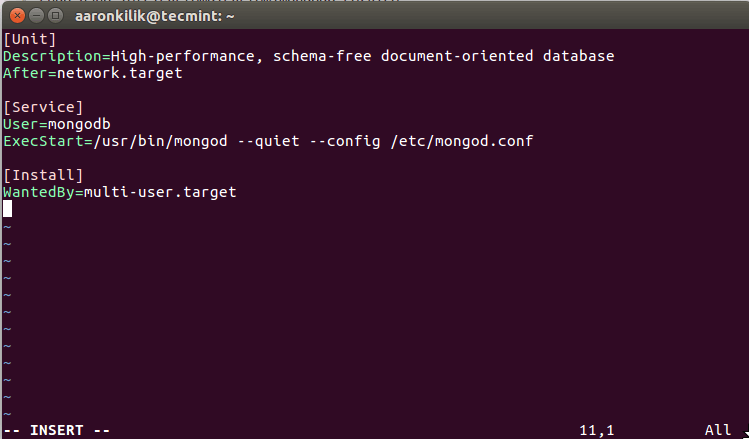
Since the mongodb user is in the mongodb group but does not own the file, it cannot write. sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/rvice paste this: Unit DescriptionHigh-performance, schema-free document-oriented >database Afternetwork.target Service Usermongodb ExecStart/usr/bin/mongod -quiet -config /etc/nf Install WantedBymulti-user.target finally. Given your current permissions: the owner is ubuntu which can rwx read, write, and execute, while the group is mongodb which can only r-x read, execute. At the end of the installation, enable and start the MongoDB service. If this is the case, then the user mongodb needs permission to write to the directory. Next, refresh the APT command to synchronize all repositories.
My server here is running 3.4.15 but I tested with 3.14.18 from, I'm guessing in this case mongodb runs as the user mongodb
#MONGODB SERVICE START UBUNTU HOW TO#
In this article, you learned How to Install MongoDB on Ubuntu 20.04 by finishing the steps of this guide and now you added the official MongoDB repository to your APT instance and installed the latest version of MongoDB. Log_size=2GB),statistics_log=(wait= 0 ),verbose=(recovery_progress),Ģ018 - 11 -22T12: 25 : 38.052 + 0000 I STORAGE WiredTiger message, txn-recover: Main recovery loop: starting at 5591 / 38323200Ģ018 - 11 -22T12: 25 : 38.174 + 0000 I STORAGE WiredTiger message, txn-recover: Recovering log 5591 through 5592Ģ018 - 11 -22T12: 25 : 38.232 + 0000 I STORAGE WiredTiger message, txn-recover: Recovering log 5592 through 5592Ģ018 - 11 -22T12: 25 : 55.956 + 0000 I STORAGE Starting WiredTigerRecordStoreThread Ģ018 - 11 -22T12: 25 : 55.956 + 0000 I STORAGE The size storer reports that the oplog contains 39153394 records totaling to 10711736188 bytesĢ018 - 11 -22T12: 25 : 55.956 + 0000 I STORAGE Sampling from the oplog between Nov 8 04 : 49 : 55 :1e and Nov 22 12 : 25 : 26 : 2 to determine where to place markers for truncationĢ018 - 11 -22T12: 25 : 55.957 + 0000 I STORAGE Taking 1000 samples and assuming that each section of oplog contains approximately 391418 records totaling to 107085642 bytes Run the following systemctl command to start the MongoDB service: sudo systemctl start rvice. The installation process described in the previous step. Step 2 Starting the MongoDB Service and Testing the Database. Ubuntu’s official package repositories include a stable version of MongoDB. After doing this process then go this directory root /etc/systemd/system/ and run the following command. This command will install the latest several packages for MongoDB. sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org OR sudo apt-get install mongodb. Now, run the following command to install MongoDB. To start the MongoDB automatically at each boot, the command is: sudo systemctl enable mongod.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
